Introduction
Sodium sulfate, a seemingly simple compound, plays an essential role in various industries. From detergents to textiles, its applications are vast, making it a significant compound to understand. Besides its industrial uses, sodium sulfate is also important in scientific studies and environmental applications. But what exactly is sodium sulfate, and why should we care? Let’s embark on this exciting exploration of sodium sulfate and uncover its secrets.
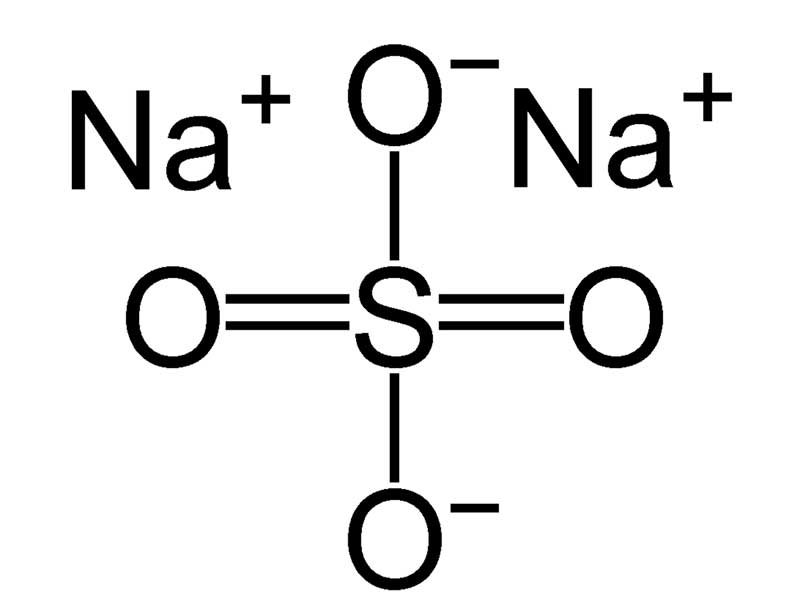
What is Sodium Sulfate?
Sodium sulfate, commonly known by its chemical formula Na2SO4, is a white crystalline solid. It’s widely found in nature and is also manufactured for various purposes. But that’s just its surface definition. This compound has fascinating properties and applications beyond what meets the eye.

Natural Occurrence of Sodium Sulfate
You might wonder where to find sodium sulfate in nature? Surprisingly, it’s naturally occurring in mineral forms such as mirabilite and thenardite. These minerals are present in arid regions, and sodium sulfate can also be found in bodies of water with high salinity.
Industrial Production of Sodium Sulfate
Industrial production methods of sodium sulfate have evolved. One common method involves the recovery of sodium sulfate from waste streams, particularly in industries like glass manufacturing. It’s also synthesized through chemical processes involving sodium chloride and sulfuric acid.
Physical and Chemical Properties
Understanding the physical and chemical properties of sodium sulfate is crucial. These properties are pivotal in determining its suitability for various applications.
Physical Properties
- Appearance: Sodium sulfate appears as a white crystalline solid.
- Solubility: It’s highly soluble in water, forming a clear solution.
- Melting Point: It has a melting point of about 884°C.
Chemical Properties
Sodium sulfate is a neutral salt, meaning it doesn’t exhibit acidic or basic properties in solutions. It undergoes a few chemical reactions, primarily those involved in the production and recovery processes.
Major Applications of Sodium Sulfate
Sodium Sulfate in the Detergent Industry
One of the most significant uses of sodium sulfate is in the manufacturing of detergents. It serves as a filler and a processing aid, enhancing the detergent’s properties without affecting its functionality.
Textile Industry Applications
In the textile industry, sodium sulfate is used during the dyeing process. It helps in even dye application, ensuring vibrant and uniform colors on fabrics.
Food Industry Insights
Ever thought sodium sulfate had a role in the food industry? While not directly used in food products, it plays a role in food packaging and the preservation of certain food items.
Glass Manufacturing
Sodium sulfate is crucial in glass production, where it serves as a refining agent. It helps remove small air bubbles from molten glass, resulting in clearer, higher-quality products.
Environmental Impact
Sustainability and Sodium Sulfate
The production and use of sodium sulfate have raised questions about environmental sustainability. Indeed, it’s less harmful than many other industrial chemicals, but it’s essential to monitor its environmental impact, particularly in ecosystems where it occurs naturally.
Waste Management
In waste management, sodium sulfate’s reuse and recycling are gaining attention. Industries focus on reducing waste and recovering sodium sulfate from industrial processes, promoting a circular economy.
Health and Safety Considerations
Even though sodium sulfate is generally safe, any compound used widely needs scrutiny under health and safety guidelines.
Handling Precautions
When handling sodium sulfate, users should avoid inhalation and direct contact with eyes and skin. Wearing protective gear in industrial settings is always advisable.
Potential Health Impacts
High exposure levels are unusual, but if it occurs, it could lead to irritation of the respiratory system, eyes, and skin. Therefore, adhering to safety data sheets and guidelines is crucial.
The Chemistry Behind Sodium Sulfate
Chemistry enthusiasts should find the reactions involving sodium sulfate intriguing. One common reaction involves sulfur dioxide oxidation, forming sodium sulfate in environmental processes.
Sodium Sulfate’s Role in Science
Laboratory Uses
Sodium sulfate acts as a desiccant in laboratories. It’s efficient and less reactive, making it ideal for drying organic solutions.
Research and Development
Researchers employ sodium sulfate in various studies, exploring its properties and potential new applications. Whether it’s crystal growth studies or environmental monitoring, sodium sulfate serves multiple purposes in research labs.
Challenges and Future Prospects
Challenges in Sodium Sulfate Usage
Despite its usefulness, sodium sulfate faces competition from alternative compounds in specific applications. The challenge is to innovate ways to process and apply it more efficiently and sustainably.
The Future of Sodium Sulfate
In the future, sodium sulfate may find expanded roles, particularly with growing environmental regulations and industrial shifts towards greener practices.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is sodium sulfate primarily used for?
Sodium sulfate is primarily used in detergents, textile dyeing, glass manufacturing, and as a drying agent in laboratories. - Is sodium sulfate a natural or synthetic compound?
Sodium sulfate occurs naturally in mineral forms but is also produced synthetically for industrial purposes. - What are the safety precautions for handling sodium sulfate?
Use protective gear to avoid skin and eye contact, and avoid inhalation. It’s wise to follow the manufacturer’s safety guidelines. - How does sodium sulfate affect the environment?
It’s relatively low in toxicity, but large amounts can impact ecosystems. Hence, monitoring and responsible waste management are advocated. - Can sodium sulfate be found in food?
It’s not directly used in food products, but it aids in food processing and packaging. - What are some alternatives to sodium sulfate in industrial applications?
Alternatives depend on the application. For example, in detergents, alternatives could include other salts or fillers based on cost and efficiency.
Conclusion
Sodium sulfate, with its multitude of uses and significant impact across industries, remains a vital compound worth exploring and understanding. Despite the challenges related to environmental concerns and competition from alternative products, sodium sulfate holds promise for future applications. As science and industry evolve, so too will sodium sulfate’s role, adapting to meet the world’s ever-growing needs. Whether you’re a chemistry geek, an industrial professional, or an environmental enthusiast, sodium sulfate surely deserves your attention.





No comment